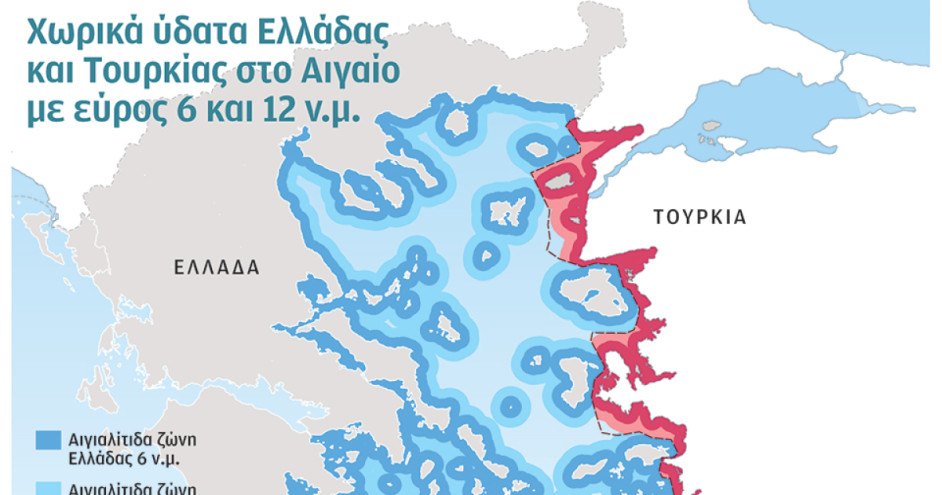
In the 1st episode of SKAI’s new Podcast series, Angelos Syrigos, Professor of International Relations, explains what a coastal zone means, what is different with 6 with 12 nautical miles and how Turkey’s Casus Belli emerged.
With the Turkish side pursuing and constantly triggering tension in Aegeanwe hear and read on a daily basis now for words such as EEZ; shelf; gray zoneseven territorial waters. Words that have been unknown to us so far or at least confused in our minds. How sure we are that we know accurately what each of them mean?
In this New Podcast 4 episode series of SKAI entitled ‘The alphabet of Greek -Turkish relations“, The journalist Stefanos Nikolaidis He discusses with the Professor of International Relations of Panteion University and ND MP, Angelfor the importance of basic and fundamental concepts around the Greek -Turkish relations.
Episode 1: Spatial Waters and Aegeal Belt – The Casus Belli
To episode of the series, Angel Syrigos explains in a comprehensible and understandable manner What does coastal zone mean; What are 6 with 12 nautical miles differentas well as How did Turkey’s Casus Belli come about.
You can hear the whole episode here.
Coastal zone = territorial waters
The Aegean emerged as Turkey’s strategic move when it made the invasion of the island to create a second front in Greece. Until ’74 the only thorn between Greece and Turkey and the main reference issue was Cyprus and the second was the two minorities, the Muslim in Greece and the Greek in Turkey.
Creating a second front in Greece, Turkey has made Greece now deal with two issues, so from ’74 onwards this issue begins. And is a fact that it starts with the territorial waters.
The concepts’territorial waters“,”territorial waters“Or“spatial sea»They are absolutely identical.
Territorial waters It is an area that starts off the coasts and extends up to 12 miles from the coasts, in which the state has sovereignty, that is, the situation is assimilated to this area with the land.
Are they absolutely alike? No, it’s not absolutely the same. On the land territory no one can “ride”, tell him “where are you going?” And answer you, “I get there from here to get to another country.” It has strict entry conditions, control of specific roads and with specific criteria.
On the contrary, in the coastal zone there is customary, that is, for many centuries, the right of crossing. That is, one can get in (even a merchant or warship), who crosses this area without getting permission from the state, if it crosses it in a certain way, that is, in a rapid way, following the line, the shortest way and avoiding making moves that cause problems in the security and defense of a state.
This is the only point that differentiates the coastal zone in terms of sovereignty over terrestrial territory and everything in the coastal zone also applies to the airspace above the coastal zone.
What are 6 with 12 nautical miles different
Traditionally, the states up to the early 20th century had 3 nautical miles territorial waters. From the beginning of the 20th century, their territorial waters are slowly expanding. Greece 1936 did 6 miles and followed by Turkey 60swhich also made them 6 miles.
The 1970 Too many states have now adopted territorial waters 12 -mile. In 1973, the third UN conference begins for the Sea lawwhich unanimously, with the exception of Turkey, accepts that there is a universal rule that territorial waters should extend to 12 miles from the coast. Indeed, since then we have a universal acceptance of this limit.
It is noteworthy that in 2009 there were 148 countries from the 152 coastal countries of the world, which had 12 miles of territorial waters. Three countries, the Montenegrothe Bosnia-Herzegovina and the Singaporethey could not extend their territorial waters over 12 miles for geographical reasons. And one country, the Greece He could extend it to 12 miles, but he kept it at 6 miles.
This situation has partially changed the 2021when Greece voted a law and expanded its territorial waters to 12 miles in its area Ionianso our country now has 6 miles to the Aegean and 12 miles in the Ionian area.
Why is the situation different from the Aegean from the Ionian Sea?
The official Greek position, as stated in the ratification law with which we accepted the Contract for sea law In May 1995, it is that Greece maintains its right to expand its territorial waters to 12 miles and will do so in the future.
There were several reasons in the past. The 1973when it was first raised as a matter, they had just begun their work at the UN and were discussing exactly that. So the Greek position was “let’s wait to see what the deal will say”.
OR Treaty on sea law signed the 1982 And he really accepted the 12 -mile territorial waters. But this agreement came into force in 1994, not in 1982 and Greece ratified her 1995.
But shortly thereafter, Turkey, with a resolution of the Great National Assembly, made a direct threat. He said that if Greece expands the territorial waters to 12 miles, this would recommend Cause of War (Casus Belli) For Turkey, because it violates the vital interests of this country.
Truth about Turkey’s Casus Belli in the Aegean
The world is the impression that Turkey first threatened us with Casus Belli in 1995 with the resolution of the Great Turkish National Assembly. It’s not true that.
The first time he was said was at June 9, 1974when there was tension between the two countries around the shelf issues, when the Turkish government spokesman said the two countries would clash warn if needed to increase Greek territorial waters to 12 miles.
This position changed with the passage of years. While it was “we do not want Greece to increase its territorial waters to 12 miles”, then it became “we do not want Greece to increase its territorial waters beyond 6 miles”.
Casus Belli is a completely illegal act. Contradicts basic rules of international law and for accuracy in Article 2 (4) of Charter of UNwhich states that states in their relationships should avoid the use of violence or threat of violence. In this sense, it is a completely illegal move. Beyond that, however, it is a threat that you have to keep in mind, not to cancel your plans, but to take your steps so that when you move on to such a move, to prevent the possibility of war.
What about Greece -Turkey airspace
The 1936 Greece expanded its territorial waters in 6 miles, but 5 years ago, 1931had stipulated that the air space extends her to 10 miles.
To clarify something. When these things happened, the concepts of airspace and territorial waters were still in progress. In 1931 the aviation was still in its first steps and it was no strange that the airspace was more than the territorial waters.
Over the years Greece has never been identified by the airspace with territorial waters And so we still have 6 nautical miles of territorial waters and 10 nautical miles. This is a point justified by international law.
Somehow a ‘one has been created’ ‘international custom»In the Aegean region, but it is a point that Turkey exploits very much, saying there is no other country in the world in which, while you are in the 7 miles off the coast of a state, if you are in the sea, you are in an international area . If you get into the air, however, you violate the Greek national airspace.
This is something we need to see, because it also creates a sense of graphics sometimes in Greek -Turkish relations.
How is this solved? Is solved with expanding territorial waters in order to identify with airspace.
The Athens FIR and Turkish challenges
The FIR are the initials of Flight Information Region, that is, it means’Flight area“
After 1944 created the International Air Navigation Organizationwho split the planet into large areas and to subjugation. In these sub -hosts he created a Center for Air Traffic Local Control, so that aircraft do not collide with each other. Some countries, Italy, for example, can have three such flight centers.
OR Greece has a flight information center, the FIR Athens, while the Turkey Has in Constantinople the Istanbul fir and in Ankara the Ankara fir.
What are they doing? They do not exercise sovereignty. They exercise an administrative competence. Direct the planes not to collide with each other.
How did the problem with the Athens FIR arose? The boundaries of the FIR Athens are the boundaries of the eastern Aegean islands. Turkey had agreed on this when the issue was first discussed 1952.
The 1974, But when problems began in Greek -Turkish relations, Turkey called for the limits to be informed if an airplane has entered the Turkish airspace from the boundaries of the eastern islands in the middle of the Aegean. He wanted to arbitrarily expand the FIR of Constantinople in the middle of the Aegean. This was not accepted by Greece. In any case, it was a matter of international agreement.
It is one of the few issues that Turkey was forced to retreat. However, it is a matter that is always there. Turkey does not accept the FIR of Athens FIR and often sends aircraft inside which violate air traffic ruleswithout informing the Athens FIR, so there are problems with air circulation and conflicts can be created.
Source: Skai
I have worked in the news industry for over 10 years. I have been an author at News Bulletin 247 for the past 2 years. I mostly cover politics news. I am a highly experienced and respected journalist. I have won numerous awards for my work.