The significant effectiveness of vaccination with a booster dose even against infection with SARS-CoV-2 in the time period when the highly contagious Omicron strain dominated in our country, is highlighted by the latest research data.
Specifically, from December 20, 2021 to January 30, 2022, the number of cases, the number of deaths and new intubations per 100,000 population per week were estimated separately for the groups of the unvaccinated or partially vaccinated and those vaccinated with a booster dose.
The above period concerns the period in which the Omicron executive dominated in Greece.
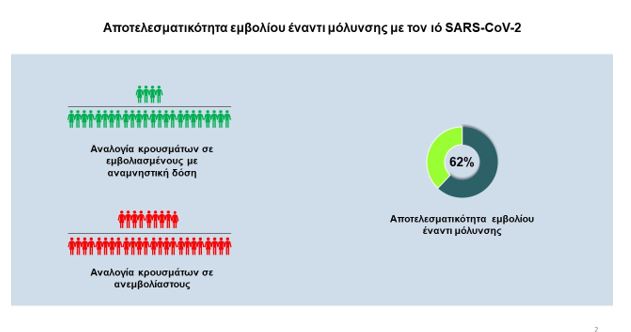
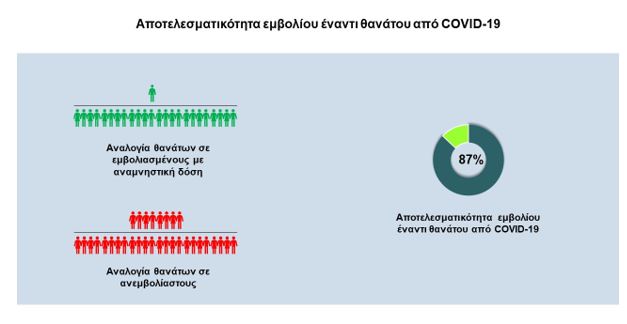
According to the data analysis, the efficacy of the booster dose of the vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infection was estimated at 62% compared with the unvaccinated or partially vaccinated, while the efficacy of the booster dose was 87% and 91% against death. from COVID-19 and intubation, respectively, in relation to the unvaccinated or partially vaccinated.
Analytically:
A. Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccine efficacy in booster vaccines relative to unvaccinated or partially vaccinated
Impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection
– The incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection was estimated at 694 cases per 100,000 vaccinated with a booster dose per week
– The incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection was estimated at 1,826 cases per 100,000 unvaccinated or partially vaccinated per week
Vaccine efficacy (booster dose) against SARS-CoV-2 infection was estimated at 62% compared with unvaccinated or partially vaccinated
B. COVID-19 mortality rate and vaccine efficacy in booster patients compared to unvaccinated or partially vaccinated
Mortality rate from COVID-19
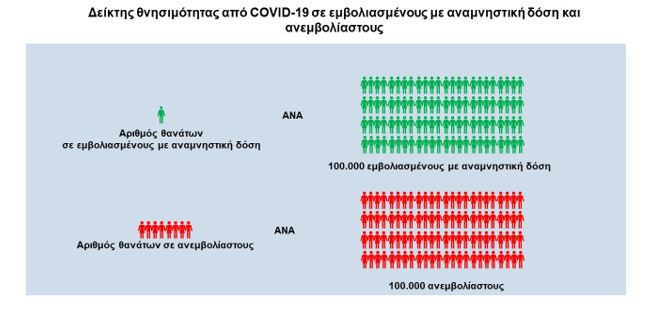
– The COVID-19 mortality rate was estimated at 1.5 deaths per 100,000 population vaccinated with a booster dose per week
The COVID-19 mortality rate was estimated at 11.7 deaths per 100,000 population unvaccinated or partially vaccinated per week
Efficacy of the vaccine (booster dose) against death from COVID-19 was estimated at 87% compared with unvaccinated or partially vaccinated
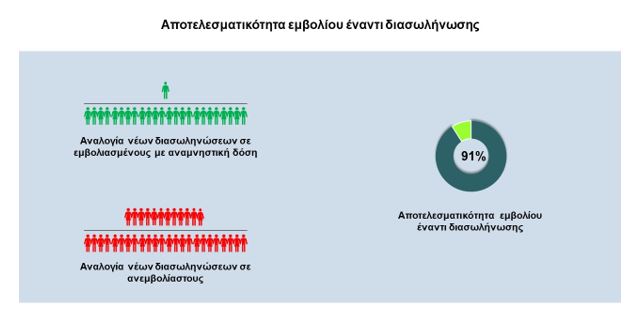
C. Impact of intubation and vaccine efficacy versus intubation in booster vaccines relative to unvaccinated or partially vaccinated
Impact of intubation
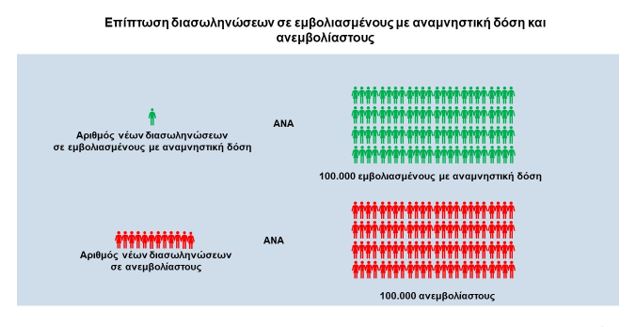
– The incidence of COVID-19 intubation was estimated at 0.5 cases per 100,000 vaccinated with a booster dose per week
The incidence of COVID-19 intubation was estimated at 6 cases per 100,000 unvaccinated or partially vaccinated per week
Vaccine efficacy (booster dose) against COVID-19 intubation was estimated at 91% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated
The above results confirm the significant efficacy of booster vaccination even against SARS-CoV-2 infection in the period dominated by the Omicron strain in the country.
It should be noted that the strain has immune escape characteristics, i.e. the ability to infect individuals who have been vaccinated or previously infected with other strains of the virus, and therefore the estimated efficacy (62%) against SARS-CoV-2 infection is characterized as particularly satisfactory.
The efficacy of booster vaccination is even greater against severe disease (intubation) and death, indicating the great advantages of vaccination against a strain with many mutations and the ability to escape pre-existing immunity.
Follow Skai.gr on Google News
and be the first to know all the news