Rising temperatures in the Arctic causes prolonged heatwaves, cold periods, droughts and more intense thunderstorms throughout the northern hemisphere
The Arctic, the frozen landscape at the top of our planet that has always fascinated humanity, and scientists are deeply concerned about its future, as the Trump government withdraws the US from the global climate strategy and leads to their scientific services.
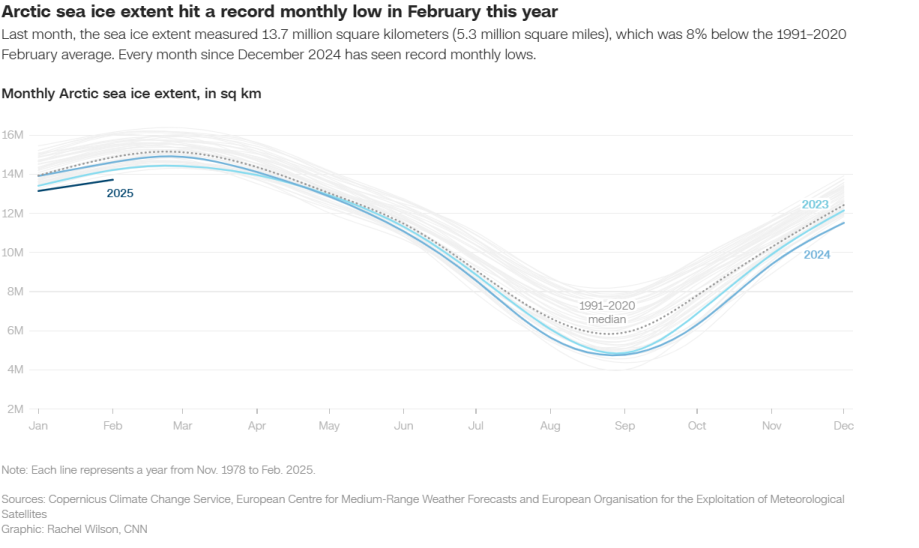
Last month, temperatures in parts of Arctic went up by 36 ° F (20 ° C) Above the normal average, and by the end of February, marine ice levels recorded the lowest historical level for the month, marking the third consecutive month with a low price record. This extreme heat And the loss of ice follows a worrying year during which the Arctic suffered severe fires, thawing of frozen soil and greenhouse gas emissions, creating the image of an area in decomposition.
The Arctic has always played a crucial role in regulating the climate of the Earth,
“It’s something like a natural air conditioner on our planet“, Said Twila Moon, Deputy Chief Scientist at the National Snow and Ice Center.
Helps in Stabilization of global temperatures And the weather systems, and her ice reflects the sunlight back in space. However, as the Arctic is heated about four times faster than the global average, this sensitive balance is disturbed. This overheating has caused the loss of sea ice, increase ocean temperature and significant changes in weather systems. According to the US Ocean and Atmospheric Service (NOAA), the area is now in a “new regime”, where extreme conditions, such as the loss of ice and the warmer temperatures of the oceans, are becoming more and more frequent, even if the records do not always break.
The impact on the global level
The consequences of these changes are global. The Arctic is already experiencing summers without some ice, with scientists warning that the area could be without any ice in the summer as early as the 2050s, perhaps earlier.
“The Arctic will be ice -free in summer sometime until 2050, even if people stop exacerbating greenhouse gases“, According to a report co -authored by Dirk Notz, head of the sea ice at the University of Hamburg. “It’s basically late to prevent it“, He told CNN
Reduction of sea ice is particularly alarming because the ice acts as a huge mirror, reflecting the sunlight back in space. As the ice melts, the darkest water water absorbs more heat, which enhances the global warming effect. This cycle accelerates the melting process and intensifies the rate of growth of warmth around the world.
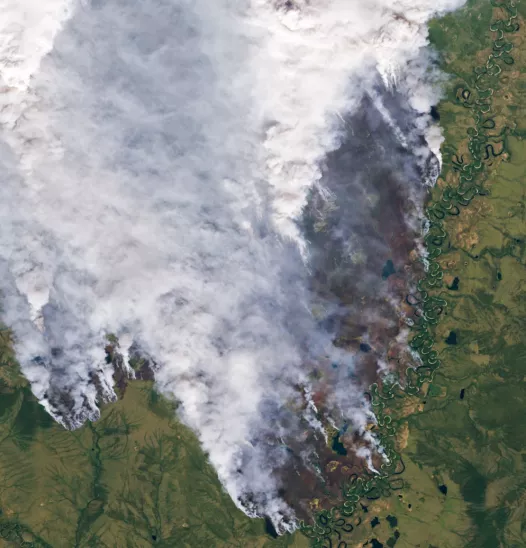
In addition to the loss of sea ice, the Arctic also faces the thawing of frozen soil – a paw that includes soil, rocks and sediments – which has stored carbon for thousands of years. As frozen ground melts, it releases greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere, further exacerbating the global warming. The Arctic also experiences more frequent and more intense fires, which last longer and are more devastating. In 2023, for the third time in five years, significant fires have occurred throughout the area. Historically, the Arctic Tudra has stored carbon, but now it is an area that releases more atmospheric pollutants than it absorbs, which exacerbates the phenomenon of climate change.
These changes alter the Arctic ecosystem, with serious Impact on Wildlife and about 4 million people living in the area. Loss of sea ice, thawing of frozen soil and increasing fires dramatically transform the landscape. Greenland’s ice cream, which is already losing about 280 billion tonnes of ice each year, contributes significantly to the rise of sea level. This has serious consequences for the world coasts, with some estimates indicating that only Greenland’s ice cream could eventually cause several meters to rise.
In addition to environmental impacts, Arctic warming affects weather systems around the world. Arctic heating weakens the flow of jet stream, which leads to more persistent weather situations. This causes more prolonged heatwaves, cold periods, droughts and more intense thunderstorms throughout the northern hemisphere. Scientists have warned that this can disrupt agriculture, water supply and overall weather stability for billions of people.
What can we do?
While some of these changes could slow down or even reversed whether global greenhouse gas emissions are drastically reduced, many of the changes occurring in the Arctic are considered “relatively irreversible“, According to experts. The overheating of the region is something that cannot be easily overturned, and the consequences will remain for centuries, if not for thousands of years.
In addition to environmental and climate impacts, there is another challenge: the ability to monitor and study the Arctic in the Arctic is becoming increasingly difficult. Geopolitical tensions, such as Russia’s war in Ukraine, have led to the split of international scientific cooperation. Russia, as Arctic’s largest country, has been ruled out by global research partnerships, which has undermined scientists’ ability to monitor changes in the region. In the US, significant cuts in climate science budgets during Trump’s rule have exacerbated the situation, reducing the ability to collect data and understand the full extent of changes in the Arctic. As Dirk Notes, a scientist at the University of Hamburg, notes, the reduction of scientific expertise and surveillance capabilities makes it much more difficult to understand the complex dynamics of the area at a time when there is such a rapid change.
What happens in the Arctic is one of the clearest and most worrying indications of how much human activities affect the planet. The constant loss of ice, the thawing of frozen soil and the changes in the weather systems highlight the urgent need for global action against climate change. The Arctic is not just a distant, frozen area – it is a critical warning signal for the whole world, and its fate will affect us all. The need for coordinated global action to slow climate change has never been more urgent.
Source: Skai
I have worked as a journalist for over 10 years, and my work has been featured on many different news websites. I am also an author, and my work has been published in several books. I specialize in opinion writing, and I often write about current events and controversial topics. I am a very well-rounded writer, and I have a lot of experience in different areas of journalism. I am a very hard worker, and I am always willing to put in the extra effort to get the job done.